With the rapid development of the photovoltaic industry, installed capacity is increasing. In some areas, the installed capacity is saturated, and newly installed solar systems are unable to sell electricity online. Grid companies are requiring that grid-connected PV systems built in the future be backflow-proof power generation systems.
What is Counterflow?
What is reverse current? In a PV system, electrical energy is generally delivered from the grid to the load, which is called forward current. When a PV system is installed, if the power of the PV system is greater than the power of the local load, the unused power is sent to the grid. As the direction of the current is opposite to that of the conventional current, this is called ‘reverse current’. In a grid-connected two-way meter, forward power is the power delivered from the grid to the load, and reverse power is the power delivered from the PV system to the grid. A backfeed PV system means that the power generated by the PV can only be used by local loads and cannot be exported to the grid.
When the PV inverter converts the DC points generated by the PV modules into AC power, there are DC components and harmonics, three-phase current unbalance and uncertainty in the output power. When the generated power is fed into the public grid, it will cause harmonic pollution to the grid, which can easily cause the grid voltage to fluctuate and flicker. If there are many such power generation sources feeding power into the grid, the power quality of the grid will be seriously degraded. Therefore, this type of photovoltaic power generation system must be equipped with reverse current protection devices to prevent the occurrence of reverse current.
How can reverse current be prevented?
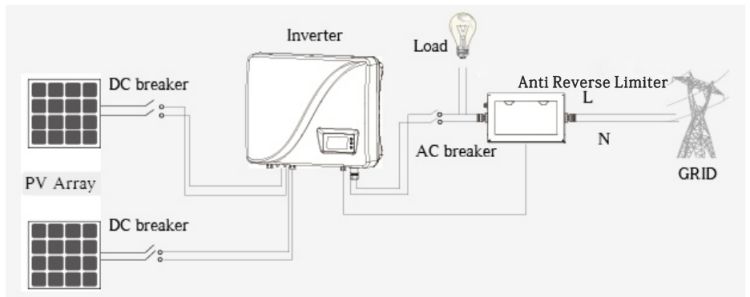
Anti-reverse current working principle: Install an anti-reverse current meter or current sensor at the grid connection point. When it detects a current flow to the grid, it sends a signal to the inverter via 485 communication, and the inverter reduces the output power until the reverse output current is zero. This realizes the anti-reverse current function. According to the different voltage levels of the system, the PV system can be divided into a single-phase anti-reverse current system and a three-phase anti-reverse current system.
How to choose an anti-reverse current smart meter?
When the PV power generation is greater than the load demand, the reverse power is generated. We need a meter to detect and determine the active power output of the inverter, and then the meter sends a signal via RS485 communication to interact with the inverter data to regulate the output power of the inverter to balance the output power and electric power.
Accuracy: Choose a smart meter that accurately measures positive and negative electricity usage. It should be highly accurate to ensure accurate billing and monitoring.
Compatibility: Check that the smart meter is compatible with your electrical system and utility requirements. It should work seamlessly with your existing infrastructure and be able to connect to the utility’s metering system.
Communication protocols: Make sure the smart meter supports communication protocols that are compatible with the utility’s network. Common protocols are Modbus, DLMS/COSEM and Zigbee.
Data management: Consider the data management capabilities of the smart meter. It should have sufficient storage space and the ability to transfer data to a centralised system for billing and analysis. Look for meters that offer data encryption and secure transmission.
Post time: Sep-08-2023