Interest in renewable energy has grown in recent years, and one of the most popular options for homeowners is to install a residential distributed photovoltaic (PV) system. This type of system harnesses sunlight and converts it into electricity, providing clean and sustainable energy for the home. For anyone considering this environmentally friendly option, it is crucial to understand the components that make up a residential distributed photovoltaic system.
The most basic component of a residential distributed photovoltaic system is, of course, the solar panel. These panels are composed of photovoltaic cells, often composed of semiconductor materials such as silicon. When sunlight hits a cell, it excites electrons, producing direct current (DC) electricity. Solar panels are typically installed on rooftops or open areas where they can receive maximum exposure to sunlight.
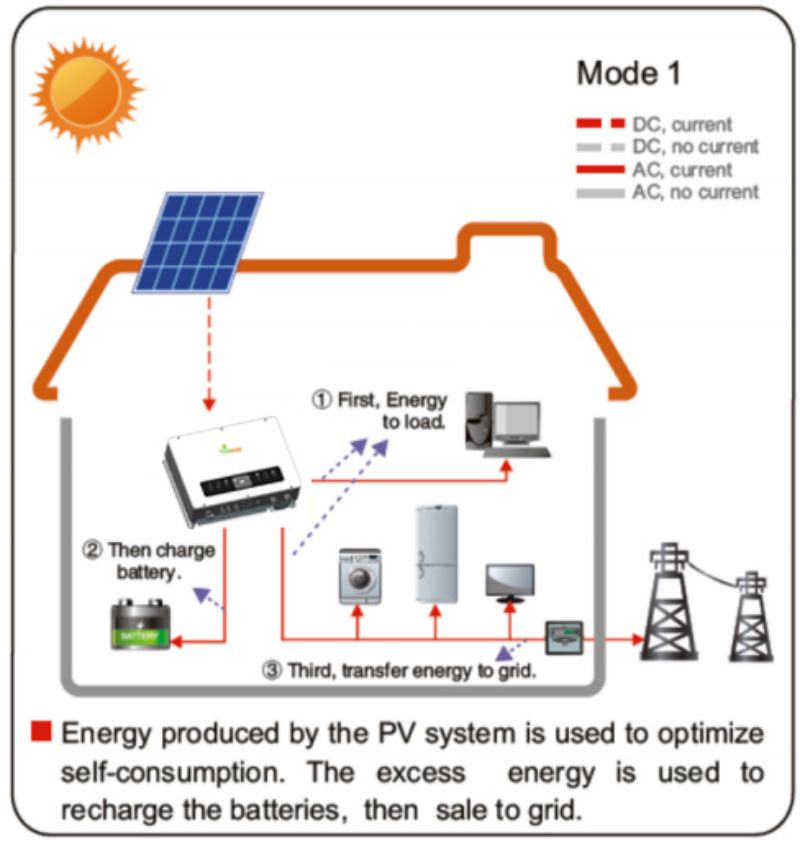
In order to harness the power produced by solar panels, the system requires an inverter. The direct current generated by solar panels needs to be converted into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes. The inverter is responsible for this conversion process, ensuring that electricity is available to power appliances and devices throughout the home.
To improve the efficiency and reliability of residential distributed photovoltaic systems, it is crucial to have a quality battery storage system. Batteries are used to store excess electricity generated during the day when demand is low so homeowners can use it when demand is high or the sun is not shining. This feature provides a degree of energy independence, reducing dependence on the grid and maximizing solar power generation.
An important component of a residential distributed photovoltaic system is the charge controller. This device ensures that the battery is charged efficiently and prevents overcharging or undercharging. It regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panel, battery and other components of the system, ensuring optimal performance and extending the life of the battery.
In order to safely distribute the electricity generated by the photovoltaic system to different areas of the house, distribution boards are required. The electrical panel acts as a central hub, connecting all the circuits in the house. It ensures that the energy from the solar panels is evenly distributed throughout the home, powering lights, appliances and other electrical equipment.
Additionally, monitoring systems are often installed for the system to operate efficiently. This allows homeowners to track the system's performance in real time, including power generation, consumption, and the battery's charge level. By closely monitoring the system, any potential issues or inefficiencies can be quickly identified and resolved, ensuring optimal performance and maximum energy savings.
Finally, in order to safely connect household distributed photovoltaic systems to the grid, grid-connected devices are required. The device allows any excess power produced by the system to be fed back into the grid, providing homeowners with the opportunity to earn points through a net metering program. It also ensures that the system operates safely and complies with all necessary regulations and standards.
In summary, a residential distributed photovoltaic system consists of several important components that work together to harness the sun’s energy and provide a clean and sustainable source of electricity to the home. From solar panels to inverters, battery storage systems, charge controllers, distribution boards, monitoring systems and grid tie-ins, each component plays a vital role in the efficient and effective operation of the system. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, understanding these components is critical for anyone considering residential distributed photovoltaic systems as a viable option to reduce environmental impact and energy costs.
Post time: Nov-24-2023